Tailieumoi.vn xin giới thiệu đến các quý thầy cô, các em học sinh đang trong quá trình ôn tập tài liệu "Lý thuyết, bài tập Unit 6 tiếng anh lớp 8" , tài liệu bao gồm 14, đầy đủ lý thuyết, phương pháp giải chi tiết và bài tập có đáp án (có lời giải), giúp các em học sinh có thêm tài liệu tham khảo trong quá trình ôn tập, củng cố kiến thức và chuẩn bị cho bài thi môn tiếng anh học kì I sắp tới. Chúc các em học sinh ôn tập thật hiệu quả và đạt được kết quả như mong đợi.
Mời các quý thầy cô và các em học sinh cùng tham khảo và tải về chi tiết tài liệu dưới đây:
Unit 6: FOLK TALES (TRUYỆN DÂN GIAN)
|
New words |
Meaning |
Picture |
Example |
|
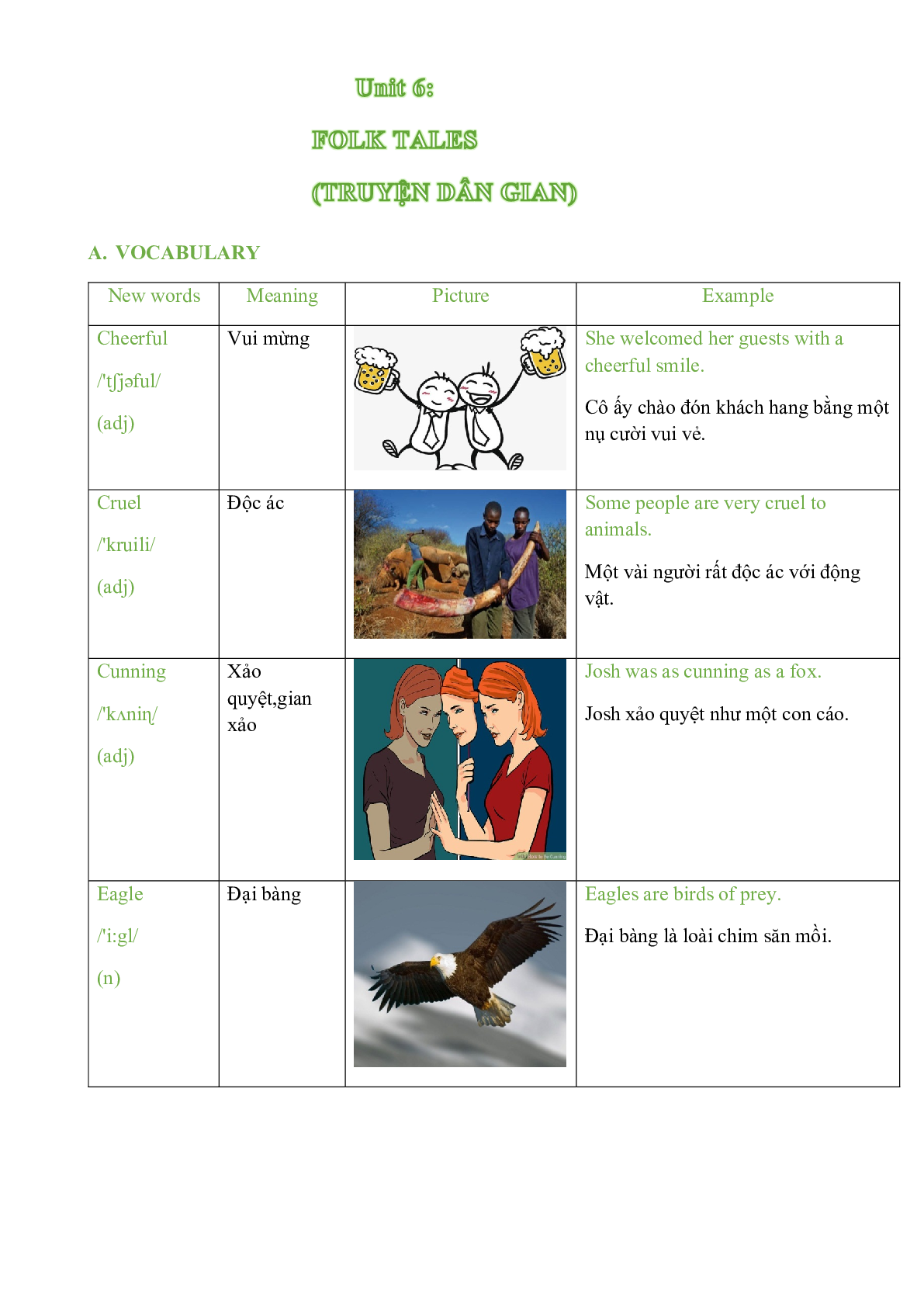
Cheerful /'tʃjəful/ (adj) |
Vui mừng |
She welcomed her guests with a cheerful smile. Cô ấy chào đón khách hang bằng một nụ cười vui vẻ. |
|
|
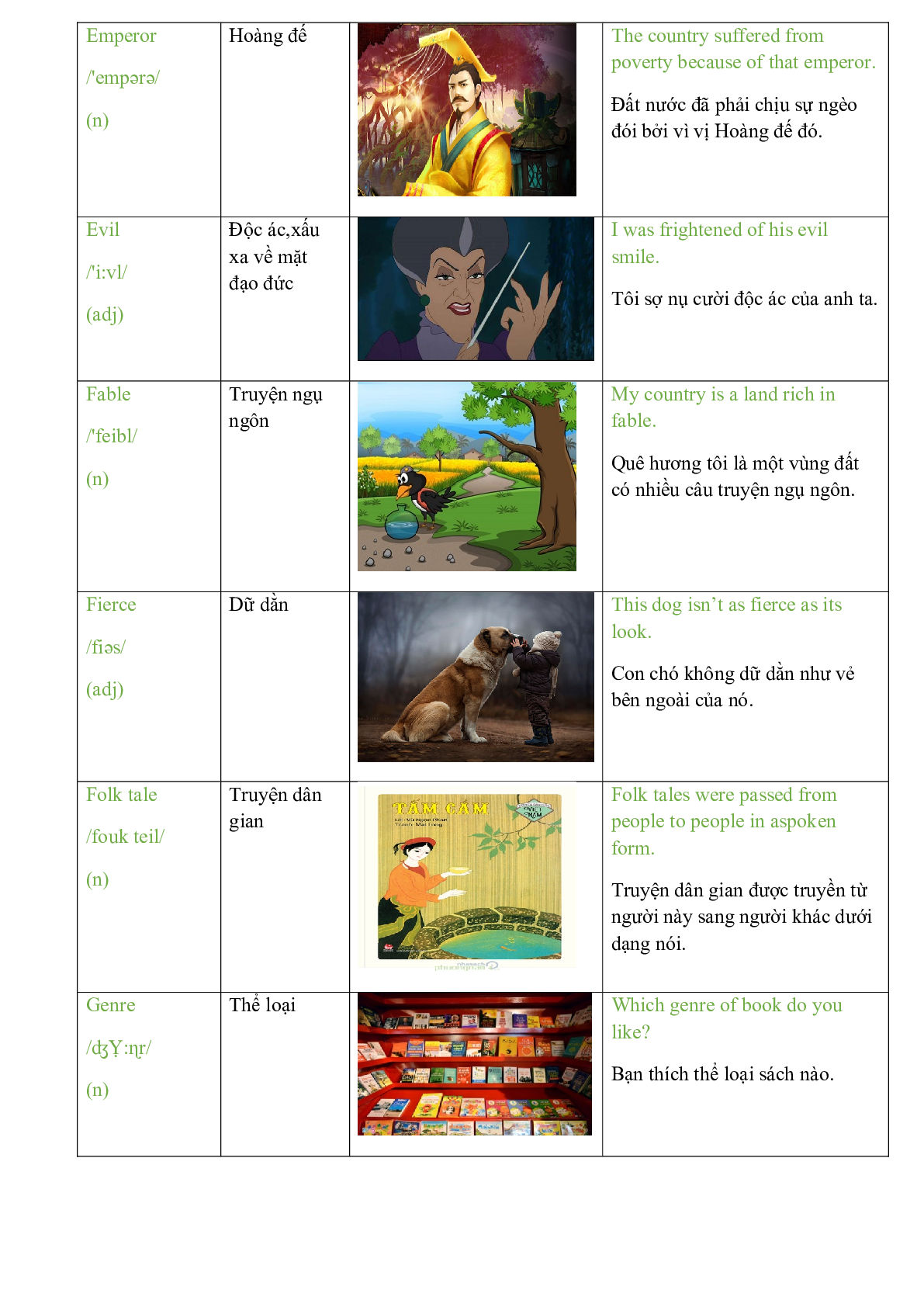
Cruel /'kruili/ (adj) |
Độc ác |
Some people are very cruel to animals. Một vài người rất độc ác với động vật. |
|
|
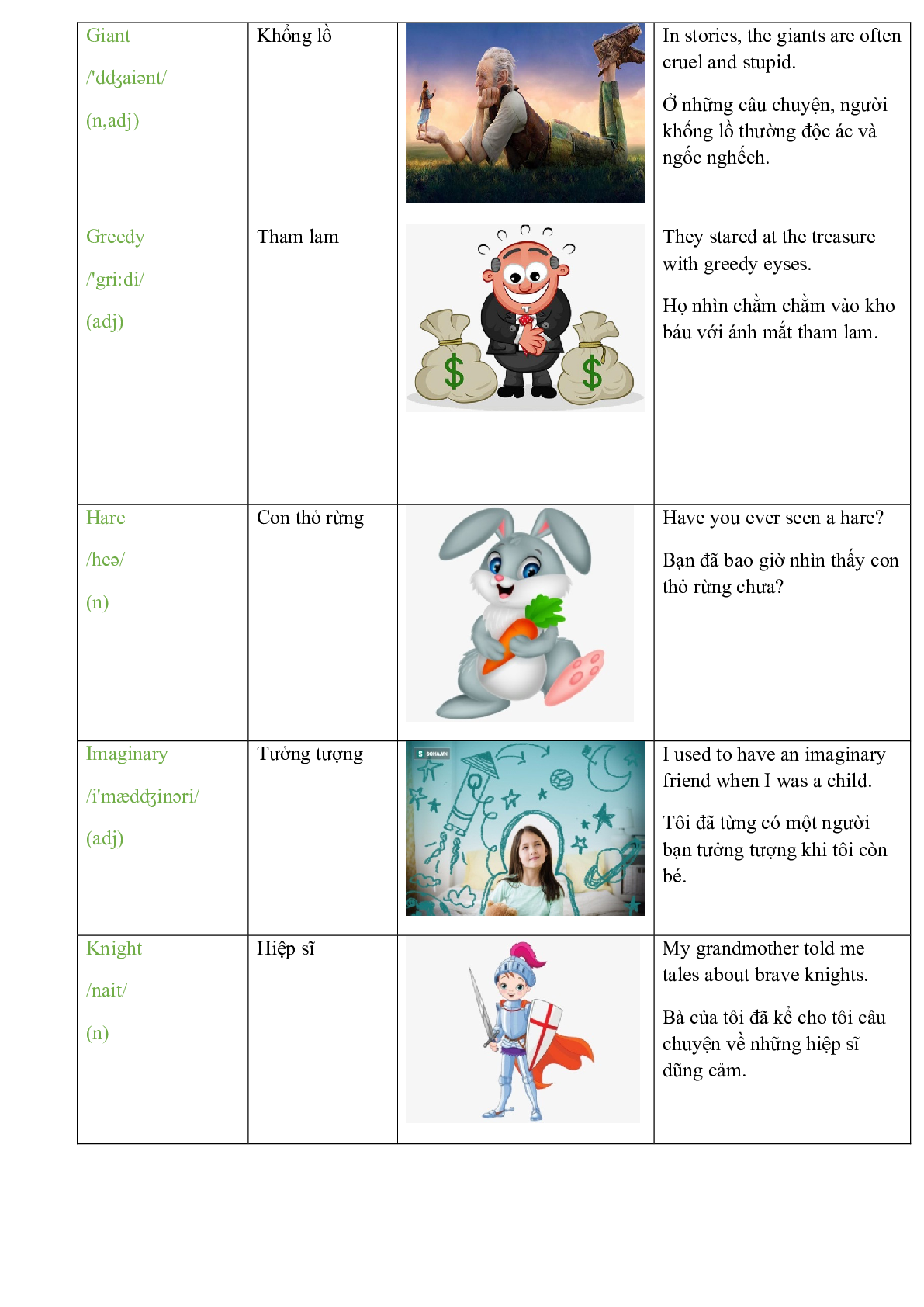
Cunning /'kʌniɳ/ (adj) |
Xảo quyệt,gian xảo |
Josh was as cunning as a fox. Josh xảo quyệt như một con cáo. |
|
|
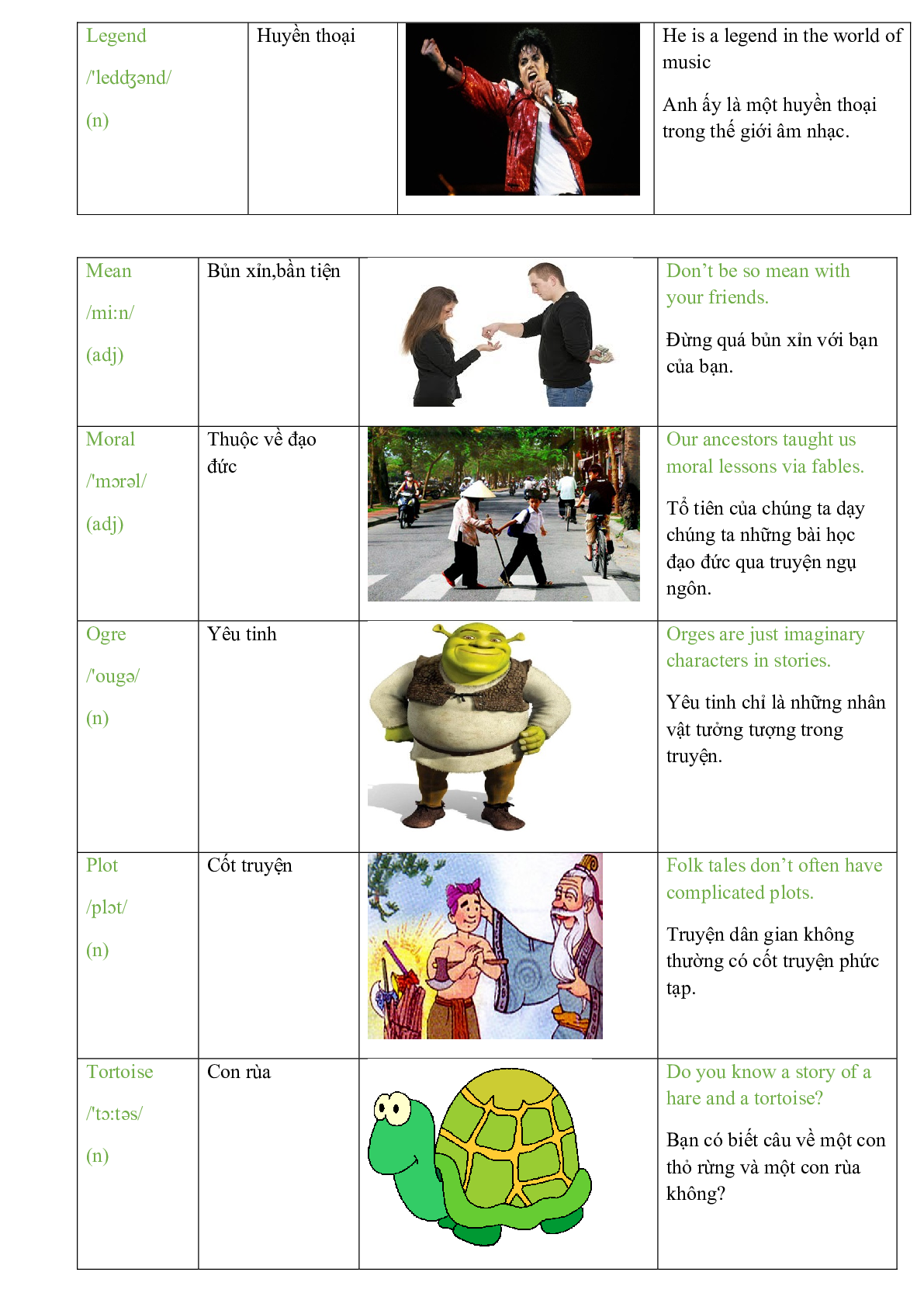
Eagle /'i:gl/ (n) |
Đại bàng |
Eagles are birds of prey. Đại bàng là loài chim săn mồi. |
|
Emperor /'empərə/ (n) |
Hoàng đế |
The country suffered from poverty because of that emperor. Đất nước đã phải chịu sự ngèo đói bởi vì vị Hoàng đế đó. |
|
|
Evil /'i:vl/ (adj) |
Độc ác,xấu xa về mặt đạo đức |
I was frightened of his evil smile. Tôi sợ nụ cười độc ác của anh ta. |
|
|
Fable /'feibl/ (n) |
Truyện ngụ ngôn |
My country is a land rich in fable. Quê hương tôi là một vùng đất có nhiều câu truyện ngụ ngôn. |
|
|
Fierce /fiəs/ (adj) |
Dữ dằn |
This dog isn’t as fierce as its look. Con chó không dữ dằn như vẻ bên ngoài của nó. |
|
|
Folk tale /fouk teil/ (n) |
Truyện dân gian |
Folk tales were passed from people to people in aspoken form. Truyện dân gian được truyền từ người này sang người khác dưới dạng nói. |
|
|
Genre /ʤỴ:ɳr/ (n) |
Thể loại |
Which genre of book do you like? Bạn thích thể loại sách nào. |
|
Giant /'dʤaiənt/ (n,adj) |
Khổng lồ |
In stories, the giants are often cruel and stupid. Ở những câu chuyện, người khổng lồ thường độc ác và ngốc nghếch. |
|
|
Greedy /'gri:di/ (adj)
|
Tham lam |
They stared at the treasure with greedy eyses. Họ nhìn chằm chằm vào kho báu với ánh mắt tham lam. |
|
|
Hare /heə/ (n) |
Con thỏ rừng |
Have you ever seen a hare? Bạn đã bao giờ nhìn thấy con thỏ rừng chưa? |
|
|
Imaginary /i'mædʤinəri/ (adj) |
Tưởng tượng |
I used to have an imaginary friend when I was a child. Tôi đã từng có một người bạn tưởng tượng khi tôi còn bé. |
|
|
Knight /nait/ (n) |
Hiệp sĩ |
My grandmother told me tales about brave knights. Bà của tôi đã kể cho tôi câu chuyện về những hiệp sĩ dũng cảm. |
|
|
Legend /'ledʤənd/ (n) |
Huyền thoại |
He is a legend in the world of music Anh ấy là một huyền thoại trong thế giới âm nhạc. |
|
Mean /mi:n/ (adj) |
Bủn xỉn,bần tiện |
Don’t be so mean with your friends. Đừng quá bủn xỉn với bạn của bạn. |
|
|
Moral /'mɔrəl/ (adj) |
Thuộc về đạo đức |
Our ancestors taught us moral lessons via fables. Tổ tiên của chúng ta dạy chúng ta những bài học đạo đức qua truyện ngụ ngôn. |
|
|
Ogre /'ougə/ (n) |
Yêu tinh |
Orges are just imaginary characters in stories. Yêu tinh chỉ là những nhân vật tưởng tượng trong truyện. |
|
|
Plot /plɔt/ (n) |
Cốt truyện |
Folk tales don’t often have complicated plots. Truyện dân gian không thường có cốt truyện phức tạp. |
|
|
Tortoise /'tɔ:təs/ (n) |
Con rùa |
Do you know a story of a hare and a tortoise? Bạn có biết câu về một con thỏ rừng và một con rùa không? |
|
|
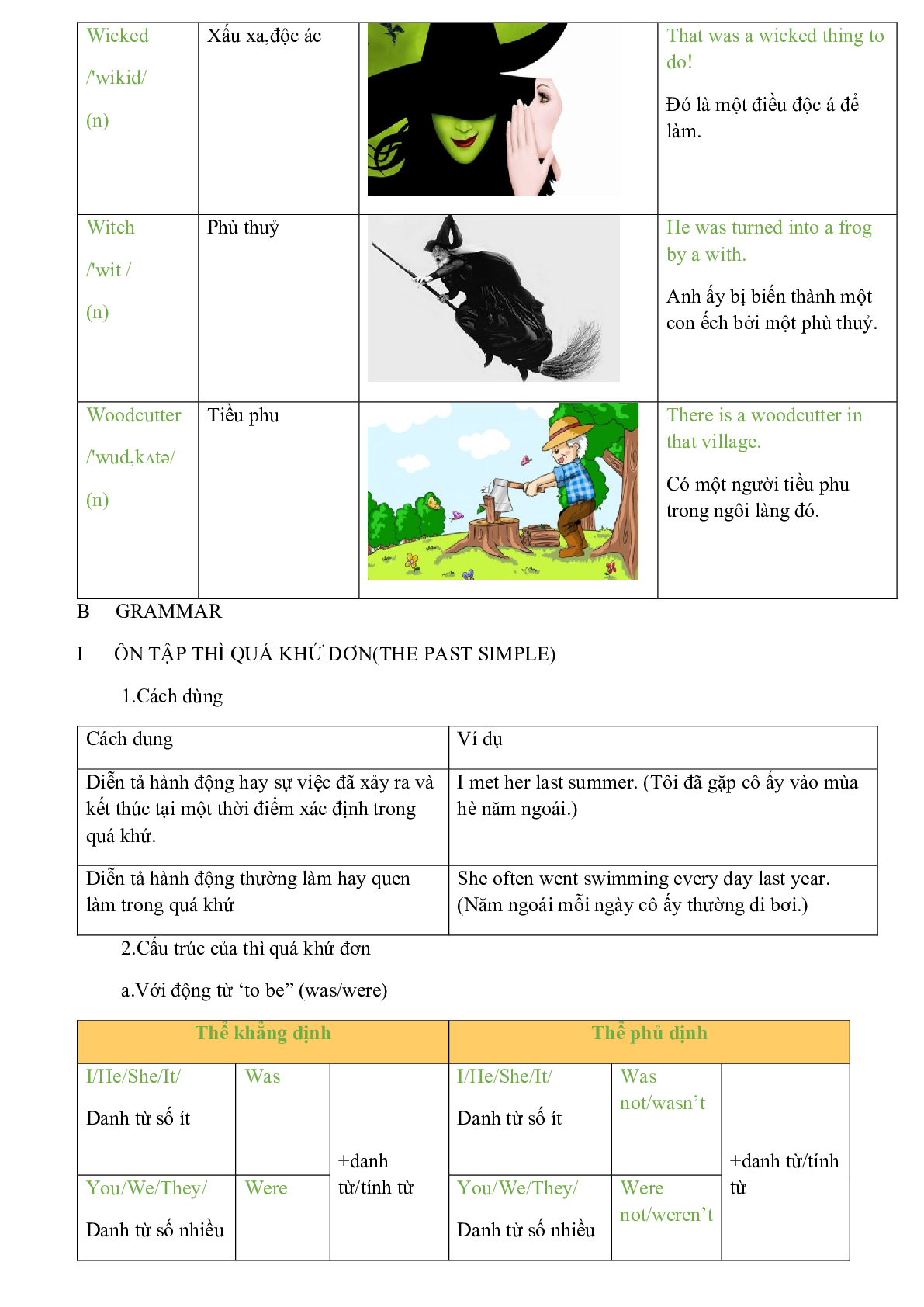
Wicked /'wikid/ (n) |
Xấu xa,độc ác |
That was a wicked thing to do! Đó là một điều độc á để làm. |
|
|
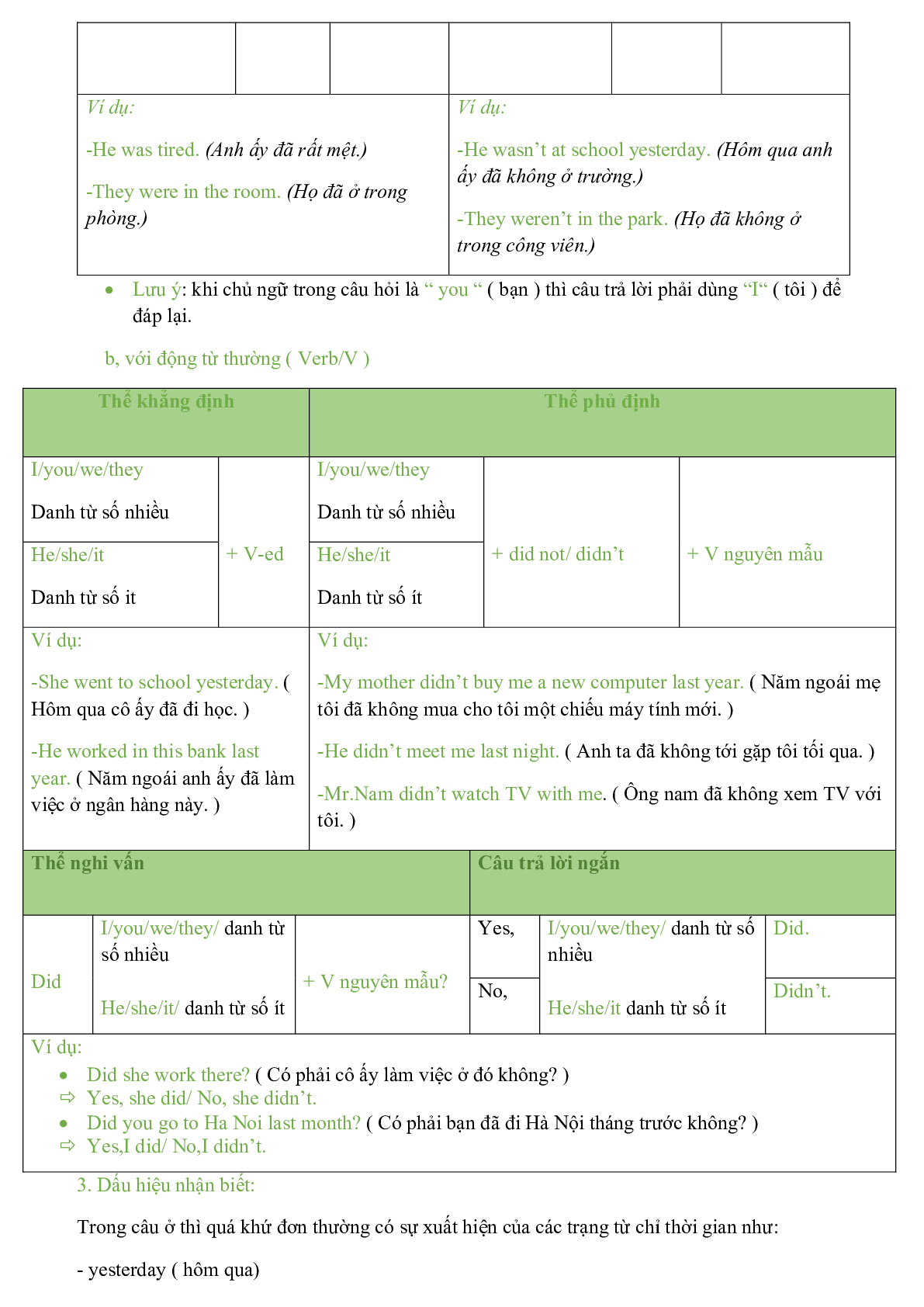
Witch /'wit / (n) |
Phù thuỷ |
He was turned into a frog by a with. Anh ấy bị biến thành một con ếch bởi một phù thuỷ. |
|
|
Woodcutter /'wud,kʌtə/ (n) |
Tiều phu |
There is a woodcutter in that village. Có một người tiều phu trong ngôi làng đó. |
B GRAMMAR
I ÔN TẬP THÌ QUÁ KHỨ ĐƠN(THE PAST SIMPLE)
1.Cách dùng
|
Cách dung |
Ví dụ |
|
Diễn tả hành động hay sự việc đã xảy ra và kết thúc tại một thời điểm xác định trong quá khứ. |
I met her last summer. (Tôi đã gặp cô ấy vào mùa hè năm ngoái.) |
|
Diễn tả hành động thường làm hay quen làm trong quá khứ |
She often went swimming every day last year. (Năm ngoái mỗi ngày cô ấy thường đi bơi.) |
2.Cấu trúc của thì quá khứ đơn
a.Với động từ ‘to be” (was/were)
|
Thể khẳng định |
Thể phủ định |
||||
|
I/He/She/It/ Danh từ số ít |
Was
|
+danh từ/tính từ
|
I/He/She/It/ Danh từ số ít |
Was not/wasn’t
|
+danh từ/tính từ
|
|
You/We/They/ Danh từ số nhiều |
Were
|
You/We/They/ Danh từ số nhiều |
Were not/weren’t
|
||
|
Ví dụ: -He was tired. (Anh ấy đã rất mệt.) -They were in the room. (Họ đã ở trong phòng.) |
Ví dụ: -He wasn’t at school yesterday. (Hôm qua anh ấy đã không ở trường.) -They weren’t in the park. (Họ đã không ở trong công viên.) |
||||
b, với động từ thường ( Verb/V )
|
Thể khẳng định |
Thể phủ định |
||||||||
|
I/you/we/they Danh từ số nhiều |
+ V-ed
|
I/you/we/they Danh từ số nhiều |
+ did not/ didn’t
|
+ V nguyên mẫu |
|||||
|
He/she/it Danh từ số it |
He/she/it Danh từ số ít |
||||||||
|
Ví dụ: -She went to school yesterday. ( Hôm qua cô ấy đã đi học. ) -He worked in this bank last year. ( Năm ngoái anh ấy đã làm việc ở ngân hàng này. ) |
Ví dụ: -My mother didn’t buy me a new computer last year. ( Năm ngoái mẹ tôi đã không mua cho tôi một chiếu máy tính mới. ) -He didn’t meet me last night. ( Anh ta đã không tới gặp tôi tối qua. ) -Mr.Nam didn’t watch TV with me. ( Ông nam đã không xem TV với tôi. ) |
||||||||
|
Thể nghi vấn |
Câu trả lời ngắn |
||||||||
|
Did |
I/you/we/they/ danh từ số nhiều
He/she/it/ danh từ số ít |
+ V nguyên mẫu? |
Yes, |
I/you/we/they/ danh từ số nhiều
He/she/it danh từ số ít |
Did. |
||||
|
No, |
Didn’t. |
||||||||
|
Ví dụ: · Did she work there? ( Có phải cô ấy làm việc ở đó không? ) ð Yes, she did/ No, she didn’t. · Did you go to Ha Noi last month? ( Có phải bạn đã đi Hà Nội tháng trước không? ) ð Yes,I did/ No,I didn’t. |
|||||||||
Trong câu ở thì quá khứ đơn thường có sự xuất hiện của các trạng từ chỉ thời gian như:
- yesterday ( hôm qua)
- last night/ week/ month ….
- ago ( cách đây)
- in + thời gian trong quá khứ ( in 1990)
- when ( khi) trong câu kể
BÀI TẬP VẬN DỤNG CƠ BẢN :
Bài 1: Chia động từ trong ngoặc ở thì quá khứ đơn để hoàn thành câu chuyện ngụ ngôn:
THE FOX AND THE GRAPES
Long, long year ago there (1. Live) ____ a fox who loved to eat. He lived close to a vineyard and he used to stare at the lovely grapes that hung there.
“ How juice they look. Oh I am sure these are stuff that metl in the mouth when you have them. If only I could reach them.” On sunny day, the fox (2. Wake)_________ up and (3.see)_______ the grapes glistening by the sunlight. The vineyard (4.look)__________ heavenly and the grapes looked so luscious that the famished fox could no longer control itself. He (5.jump)________ to reach them but fell down.
He jumped again. No, they (6.be)____ much higher.
He jumped even more. But they were still out of reach.
He jumped and (7.stretch)______ and (8.hop)_______but no avail. Those yummy grapes (9.hang)____higher than the fox could reach. No matter hard he (10.try)_______, the fox could not reach the grapes. He (11.pant)______and (12.begin)_____ to sweat out of exhaustion. Giving up finally, he looked up in contempt and (13.say)______ as he (14.walk)______away, “ those grapes surely must be sour. I wouldn’t eat them even if they were served to me on a golden dish.”
It’s easy to despisewhat you cannot have.
Baì 2: sắp xếp từ cho trước thành câu hoàn chỉnh:
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
Đánh dấu [V] trước câu đúng, đánh dấu [X] trước câu sai và viết lại câu đúng.
|
Cấu trúc |
Ví dụ |
|
Thể khẳng định I/He/She/It+ was+ V-ing We/You/They+ were+ V-ing |
I was thinking about him last night. We were just talking about it before you arrived. |
|
Thể phủ định I/He/She/It+ was not/wasn’t+ V-ing We/You/They+ were not/ weren’t+ V-ing |
I wasn’t thinking about him last night. We were not talking about it before you arrived. |
|
Thể nghi vấn Was+ I/he/She/it + V-ing? Were + We/You/They + V-ing? Câu trả lời: (+) Yes, I/He/She/It was. Yes,We/You/They were. (-) No, I/he/she/it wasn’t. No, we/you/they weren’t. |
Were you thinking him last night? What were you just talking about before I arrived.
|
Trong câu có các trạng từ chỉ thời gian trong quá khứ kèm theo thời điểm xác định.
- at + giờ + thời gian trong quá khứ ( at 12 o’clock last night, ….)
- at this time + thời gian trong quá khứ ( at this time two week ago,…)
- in + năm (in 2000, in 2005)
- in the past (trong quá khứ)
-trong câu có “ when ” khi diễn tả một hành động đang xảy ra và một hành động khác xen vào.
-while (trong quá khứ)
BÀI TẬP VẬN DỤNG CƠ BẢN
|
Chia động từ trong ngoặc ở thì quá khứ tiếp diễn để hoàn thành câu sau.
Dựa vào các từ cho sẵn, viết thành câu hoàn chỉnh.
Hoàn thành câu, sử dụng quá khứ tiếp diễn của các động từ cho sẵn.
|
Enjoy |
Paint |
rest |
read |
study |
|
Play |
Walk |
speak |
take |
vacuum |
Viết câu hỏi cho phần gạch chân trong các câu dưới đây.
Gạch chân lỗi sai và sửa lại cho đúng.
An ant and the grasshopper
In a field one summer’s day a Grasshopper was hopping about, chirping and sang to its heart’s. An Ant was passing by and he bearing along with toil an ear of corn he was taking to the nest. “Why not come and chat with me,” saying the Grasshopper, “instead of toiling and moiling in that way?”
“I am helping to lay up food for the winner,” said the Ant, “and the recommend you to do the same.”
“Why bother about winner?” said the Grasshopper; “We have got plenty of food at present.” But the Ant went on its way and was continuing its toil.
When the winner was coming the Grasshopper was having no found itself dying of hunger- while it was seeing the ants distributing every day corn and grain from the stores they had collected in the summer. Then the Grasshopper was knowing : It is best to prepare for days of need.
|
Lỗi sai |
Sửa |
Lỗi sai |
Sửa |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chia động từ trong ngoặc ở thì quá khứ đơn hoặc thì quá khứ tiếp diễn sao
BÀI 10: Dựa vào những từ cho sẵn, viết thành câu hoàn chỉnh.
1.We/ have/ breakfast/ when/ the mailman/ arrive.
Khoanh tròn đáp án đúng.
A beautiful day
Yesterday was so nice a day. Jane (1)_________ up so early. The sun (2) _______ brightly and the bids (3) ___________ on the tree. Jane was so happy because today she went to meet her old friend. Jane’s friend invited her to his new apartment with some other friends. When Jane came, everyone was sitting in the living room and (4)_________ passionately with each other. As she walked in, she (5)
by her friend. They had a lot to tell the other (6)________they had not met for ages. Jane came home with a smile on her face since her friend (7)_________ to contact regularly.
Đọc bài đọc dưới đây và điền T (True) trước câu trả lời đúng với nội dung bài đọc, điên F (False) trước câu trả lời không đúng với nội dung bài đọc.
What are myths, legends and folk tales
Once upon a time, long, long ago, there lived some really great storytellers. Their stories have been passed down, retold, translated, adapted and, more recently, written down, because everyone loves a good stories. These stories probably include, myths and folktales.
A legend is usually based on a true event in the past. Legend usually have a real hero at the centre of the story and they are often set in fantastic place. The story will have been passed on from person to person, sometimes over a very long period of time.
A myth is not quite the same as a legend. Sometimes a myth is loosely based on a real event but, more often than not, it is a story that has been created to teach people about something very important and meaningful. Myths are often used to explain the world and major events, which, at the time, people were not able to understand- earthquakes, floods, volcanic, eruptions, the rising and setting of the sun, illness and death.
Folktales are usually stories that have been passed down from generation to generation in spoken from. Often we do not know who was the original author and it is possible that some stories might have been concocted author a campfire by a whole group of people. It is quite normal to discover that are many version of the tale, some very similar but others may have only one or two characters in common and take place in totally different settings.
_____ 1.In legends, heroes are set in fantastic places.
_____ 2.Amongst legends, myths and folktales, only legends are based on true event in the past.
_____ 3.Myths are created only for entertainment.
_____ 4.Earthquakes, floods and volcanic eruptions are explained in myths.
_____ 5.Folktales may be invented around a campfire by a whole group of people.
_____ 6.Folk tales have only one version.
_____ 7.Folktales are usually passed in written form.